The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has implemented the Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) Model V28, significantly changing coding and risk adjustment methodologies for Medicare Advantage and other specific Medicare health plans. While these updates present challenges, they also offer opportunities for improved accuracy and efficiency in coding and documentation practices, potentially impacting healthcare providers’ revenue streams positively.
Is V28 an Opportunity or a Challenge?
The transition to CMS – HCC Model V24 to V28 presents both opportunities and challenges for healthcare organizations, requiring careful navigation of significant changes in coding practices and risk adjustment strategies.
1. Embracing V28: A Phased Transition for Providers
To facilitate the transition to CMS – HCC Model V24 to V28 will be gradually implemented over a three-year period. For dates of service in 2023, the model utilized a combination of 33% from V28 and 67% from V24. In 2024, V28 will account for 67% of the calculations, while V24 will represent 33%. By 2025, V28 will be fully adopted at 100%, and V24 will be completely phased out. This gradual transition allows healthcare organizations to adapt to the new model and its updated HCC categories smoothly.
2. ICD-10 Code Mapping Adjustments
The V28 model has removed 2,294 ICD-10 codes previously mapped to HCCs. This change emphasizes the critical importance of accurate and comprehensive coding, as conditions not captured by the remaining mapped codes will no longer contribute to a patient’s risk adjustment factor (RAF) score.
3. V28’s New Stance on Prevalent Conditions
Several prevalent condition categories, including Diabetes, Heart Failure, COPD, Major Depressive, and bipolar disorders, have had their HCC coefficients constrained. This means that all HCCs within these groups are assigned the same weight, potentially resulting in lower RAF scores and decreased payments for patients with these conditions compared to the previous V24 model.
Potential Impact of the Proposed Changes on RAF Scores (Based on Disease Parameters)
To illustrate the impact of these changes, let’s examine two examples:
Example 67-year-old male with diabetes
Organizations will want to identify the top HCCs amongst their patient population to examine and understand the potential impact of the two model versions.
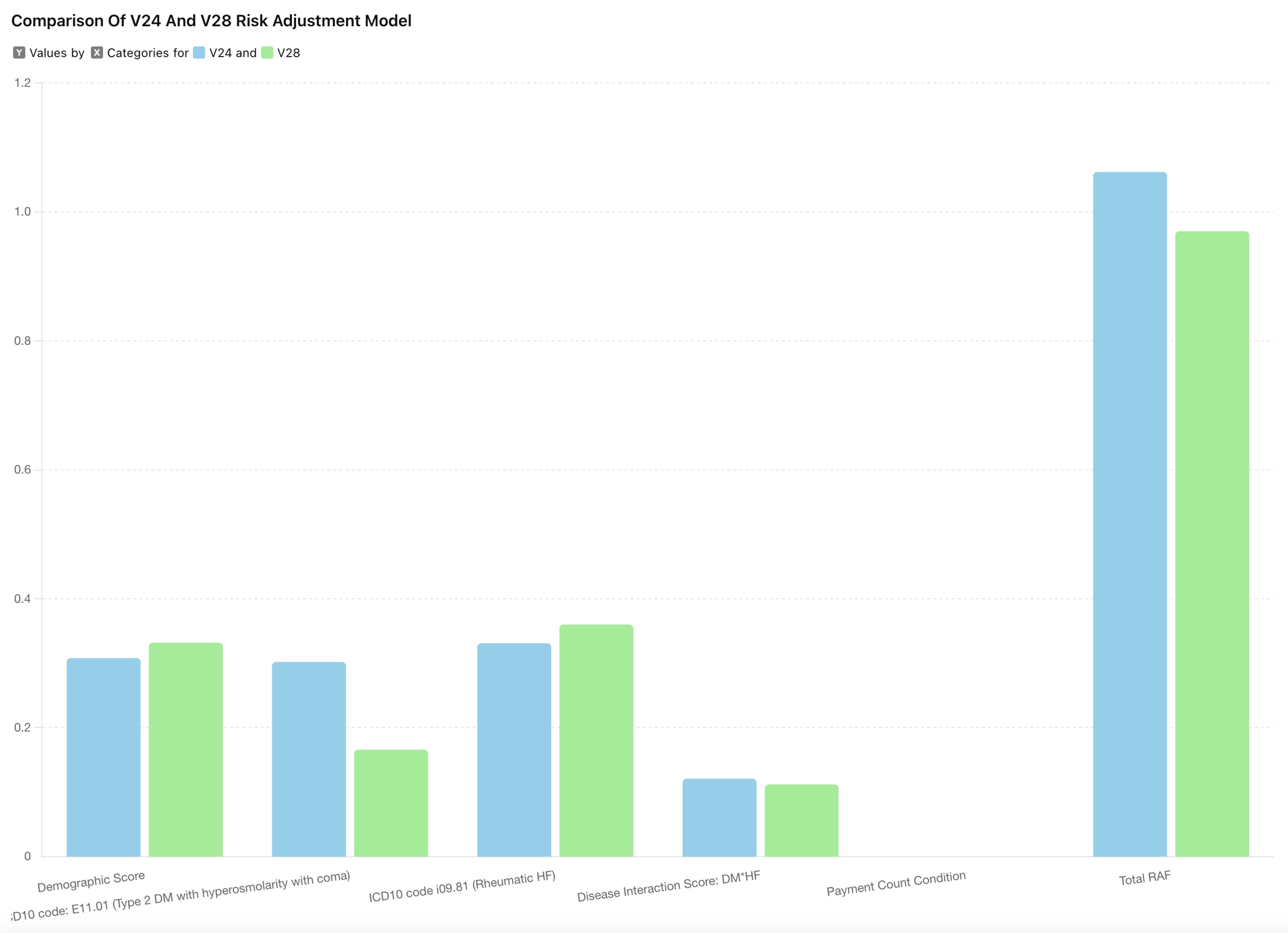
In this example, the RAF scores differ between V24 and V28 even with similar diagnoses. Notably, the total RAF score is lower in V28 (0.97) compared to V24 (1.062).
Example 2: Patient with multiple condition
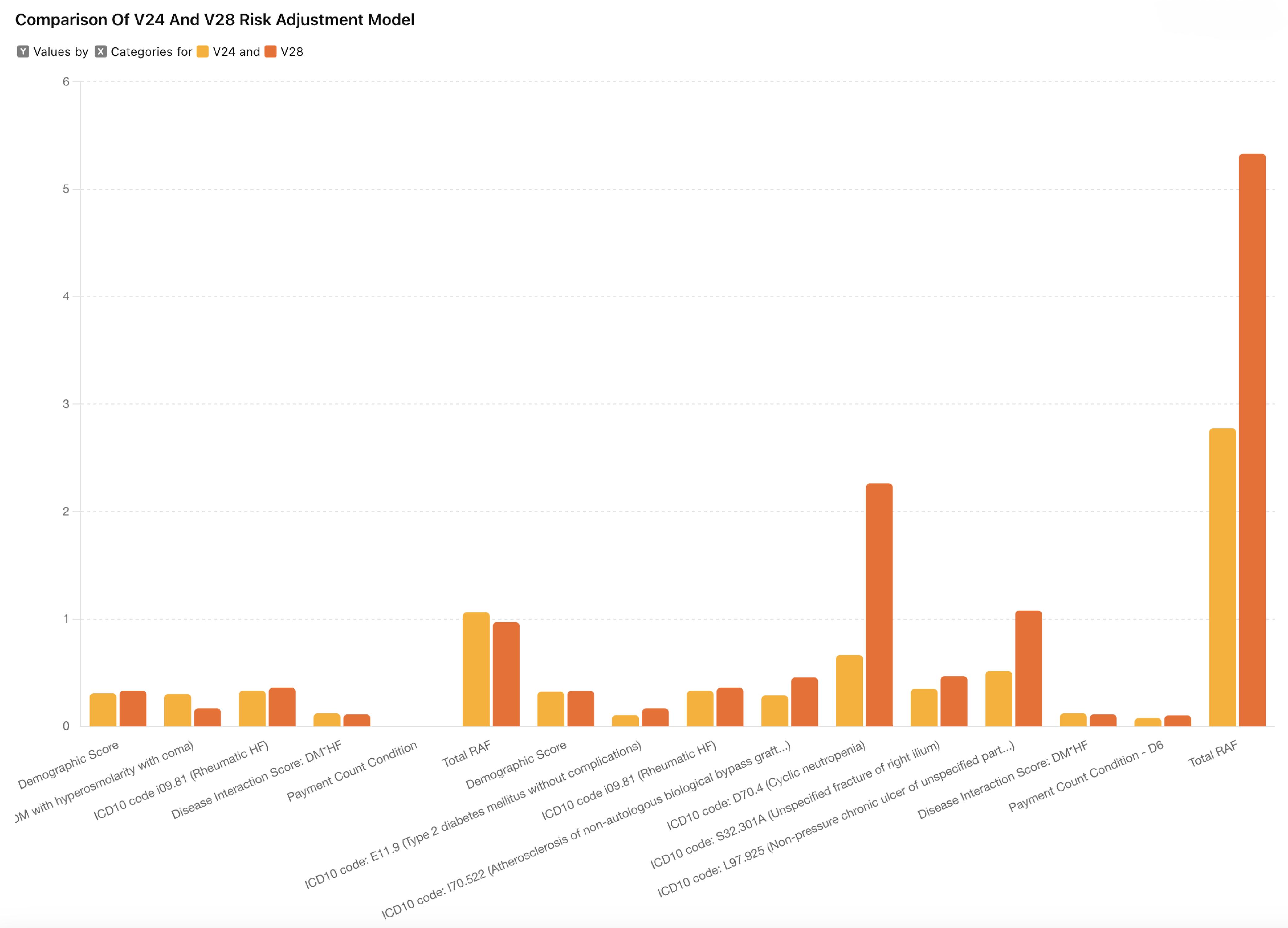
In this example, we see that even with similar diagnoses, the RAF scores differ between V24 and V28. Notably, the total RAF score is lower in V28 (0.97) compared to V24 (1.062).
This example demonstrates a significant increase in RAF score under V28 (5.332) compared to V24 (2.775) for a patient with multiple conditions. Here are the four key observations from the examples above:
• Generally, relative factors for HCCs under V28 are higher.
• The most substantial relative factors increase are immunity disorders and chronic ulcers.
• V28 applies weight to Payment Condition Categories (PCCs) only if a patient has five or more conditions.
• Relative factors for dually eligible patients remain higher in both models.
Ways to Mitigate Revenue Implications
While some HCCs have seen an increase in their coefficients, CMS predicts an overall decrease in payment of 3.12%, translating to a projected net savings of $11 billion. However, providers can take steps to mitigate potential revenue impacts:
1. Focus on Accurate Documentation
Providers must emphasize accurate and comprehensive documentation, ensuring that all relevant ICD-10 codes are captured to maximize RAF scores for patients with complex conditions.
2. Leverage High-Value HCCs
Pay special attention to conditions with higher RAF values in the V28 model, such as:
• Ulcers of Skin
• Rheumatoid Arthritis
• End-stage Heart Failure (HCC222)
• Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis (HCC278)
• And Chronic Kidney Disease, Stage 5 (HCC326)
A Robust technology Solution
For organizations to excel in V28, a robust technology solution is essential. Health IT systems can play a key role in enhancing operational efficiency, ensuring data security, and supporting strategic decision-making.
Persivia and HCC Model V28
Adapting to the CMS – HCC Model V28 requires understanding the changes and leveraging advanced technology solutions. Persivia, with 15 years of extensive experience in healthcare, enables organizations transform these regulatory challenges into opportunities with the power of AI.
Persvia supports this transition by integrating V28 changes into its solutions, ensuring a seamless implementation that minimizes operational interruptions. A phased strategy not only addresses the challenges of V28 but also offers healthcare organizations the opportunity to enhance their coding accuracy and optimize reimbursements in a value-based care environment.
Persivia CareSpace®, an AI-driven end-to-end platform, brings together data from clinical, claims, SDOH, and all other patient sources and leverages the proprietary data fabric to build a comprehensive longitudinal patient record. This precision in assigning codes that accurately reflect each patient’s clinical picture, addresses the V28 model’s emphasis on detailed documentation and complex condition interactions, reassuring the audience about the accuracy of the platform.
CareSpace® also provides real time insights and HCC opportunities at the point of care through its EHR-agnostic tool, CareTrak(R). The platform allows providers to review V28 and V24 codes side by side within the system and analyze their impact on RAF in real time.
With solutions like CareSpace®, organizations can navigate the increased complexity of the V28 model while optimizing reimbursement opportunities, ultimately balancing quality care delivery with improved financial performance.
Conclusion
The transition to the CMS-HCC Model V24 to V28 brings significant changes impacting provider revenue streams. While challenges exist, a proactive approach to coding and documentation practices, a strategic focus on high-value HCCs, can help mitigate potential revenue losses. By staying informed, leveraging technology, and adapting to these changes, healthcare providers can navigate this new landscape effectively, balancing quality care delivery with optimized financial performance.
Table of Contents
